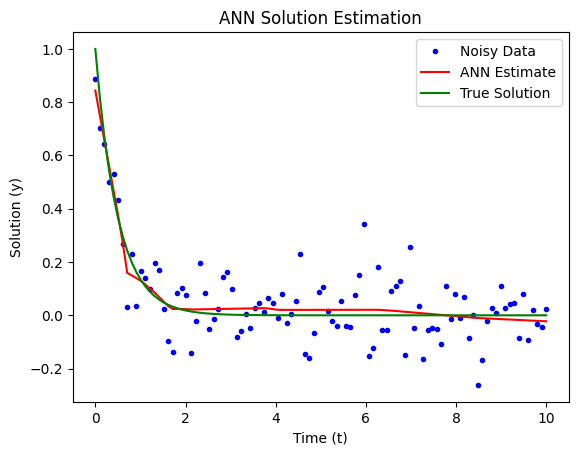
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define the initial value problem (IVP)
def f(t, y):
return -2 * y + torch.sin(t)
# Generate training data
t_data = torch.linspace(0, 10, 100).view(-1, 1) # Time values
y_data = torch.exp(-2 * t_data) # True solution to the IVP
# Create a noisy dataset for training
torch.manual_seed(0)
y_data_noisy = y_data + 0.1 * torch.randn_like(y_data)
# Define the neural network model
class NeuralNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NeuralNet, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1, 32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32, 32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
# Initialize the neural network, loss function, and optimizer
model = NeuralNet()
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# Training the neural network
num_epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Forward pass
outputs = model(t_data)
loss = criterion(outputs, y_data_noisy)
# Backward pass and optimization
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
# Estimate the solution using the trained ANN
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = model(t_data)
# Plot the true solution and the ANN's estimate
plt.figure()
plt.plot(t_data.numpy(), y_data_noisy.numpy(), 'b.', label='Noisy Data')
plt.plot(t_data.numpy(), y_pred.numpy(), 'r', label='ANN Estimate')
plt.plot(t_data.numpy(), y_data.numpy(), 'g', label='True Solution')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('Time (t)')
plt.ylabel('Solution (y)')
plt.title('ANN Solution Estimation')
plt.show()