Numerical Methods and Machine Learning for Differential Equations with Applications in Python#
This github consists of Python code corresponding to the TU Dublin module Numerical Methods and Machine Learning for Differential Equations. The aim of this module is to equip the learner with the knowledge necessary to implement computational techniques related to finite-difference methods and machine learning method for differential equations.
During the first part of the module the learner will be introduced to the theory and practice of common techniques for the numerical integration of ordinary differential equations with initial conditions. Second part will of the module the learner will be introduced to the application machine learning methods to estimate the solution of linear and non-linear ordinary differential equations. Software tools (python) will be used to implement the numerical and machine learning methods
Learning Outcomes#
Derive and apply a range of finite difference methods for solving differential equations for initial and boundary value problems.
Describe the stability, consistency, and convergence properties of various numerical integration schemes for different practical problems.
Explain the differences between various numerical methods for the integration of differential equations and identify the conditions under which they are an appropriate choice.
Describe and apply machine learning methods to approximate the solution of differential equations.
Use numerical packages to solve differential equations and interpret the results.
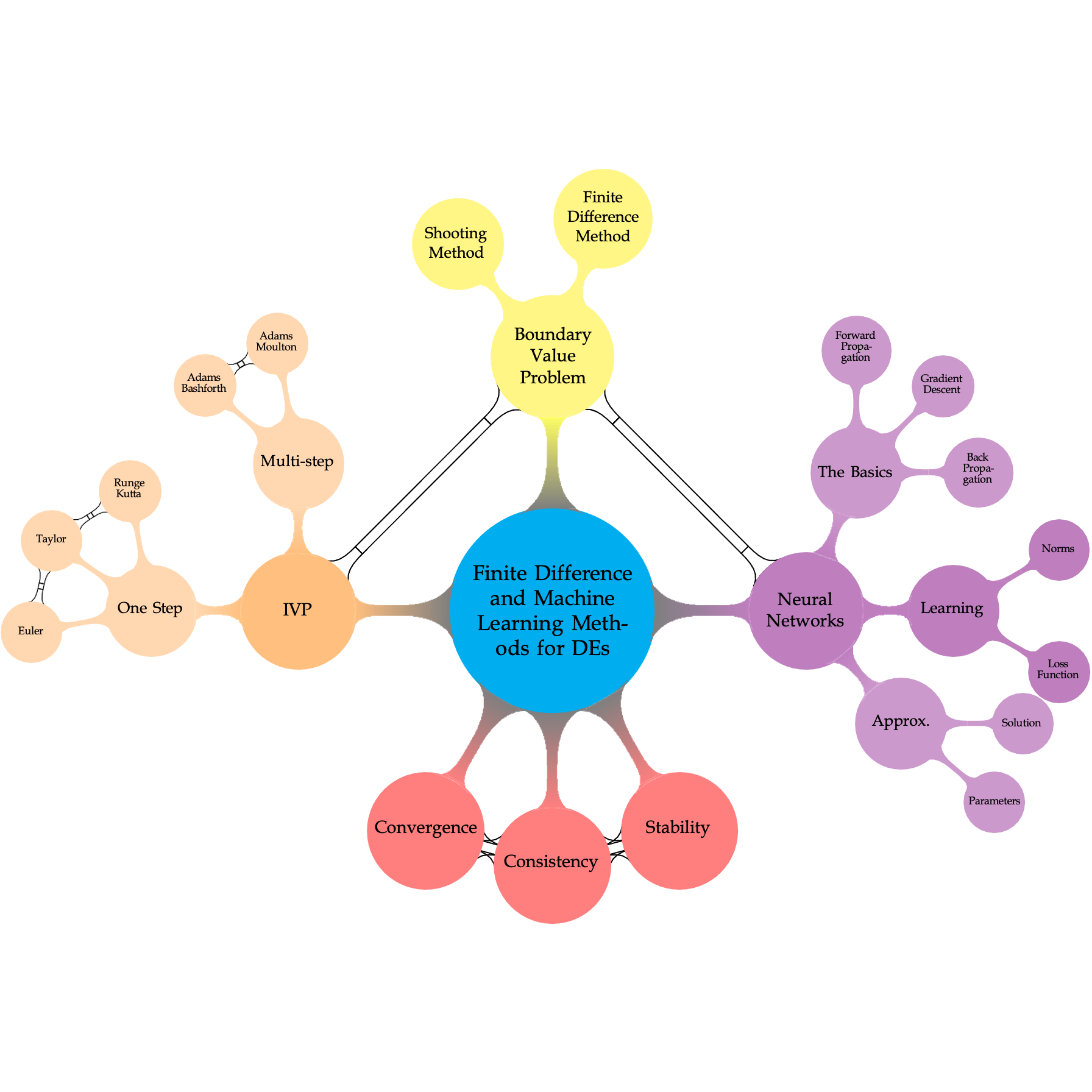
Indicative Sylabus Numerical Analysis; Finite-differencing techniques; Stability analysis; Explicit Runge-Kutta methods, multi-step methods, shoot method, convergence, consistency and stability analysis, linear shooting methods.
Machine Learning: Non-linear shooting method, Newton Raphson method; Gradient Descent; Loss functions; Norms, Forward and Back Propagation; Neural Network, The Universal Approximation Theorem for Neural Networks.
This is the JupyterBook for the code
Part 1 Numerical Solutions to Ordinary Differential Equations#
Chapter 1 Numerical Solutions to Initial Value Problems#
Chapter 2 Higher Order Methods#
Chapter 3 Runge–Kutta methods#
Chapter 4 Multi-step methods#
Chapter 5 Analsyis of Methods for Initial Value Problems#
Part 2 Numerical Solutions to Boundary Value Problems#
Chapter 6 Boundary Value Problems#
Part 3 Machine Learning methods for Differential Equations#
Chapter 7 Artifical Neural Networks#
Perceptron
Feed Forward
Loss Functions
Gradient Descent
Chapter 8 Universal Approximation Theorem#
Chapter 9 ANNs and Differential Equations#
Reading List#
Essential Reading#
[1] Brunton, S. L., & Kutz, J. N. (2019). Data-driven science and engineering: Machine learning, dynamical systems, and control. Cambridge University Press.
[2] Iserles, A., 2008, A First Course in the Numerical Analysis of Differential Equations, Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics.
Supplemental Reading#
[1] Strogatz, S. (2014) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos: with applications to physics, biology, chemistry, and engineering (studies in nonlinearity), Westview Press; 2 edition
[2] Bradie, B., (2006). A Friendly Introduction to Numerical Analysis. Pearson Education India.
[3] Atkinson, K. E., & Han, W. (1993). Elementary numerical analysis. New York: Wiley.
[4] Burden, R. L., Faires, J. D., (1997). Numerical Analysis. Brooks/Cole
[5] Stoer, J., & Bulirsch, R., (1980). Introduction to Numerical Analysis. Springer-Verlag
[6] Smith, G. D., (1992) Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations:Finite Difference Method. Oxford
[7] Sirca, S., Horvat, M., 2018, Computational Methods in Physics: Compendium for Students, Second Edition, Springer ISBN: 978-3-319-78619-3
Academic Papers#
Brunton, S. L., Proctor, J. L., & Kutz, J. N. (2016). Discovering governing equations from data by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 113(15), 3932-3937.
Cybenko, G. (1989). Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Mathematics of control, signals and systems, 2(4), 303-314.
Dufera, T. T. (2021). Deep neural network for system of ordinary differential equations: Vectorized algorithm and simulation. Machine Learning with Applications, 5, 100058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100058
t Hart, B., Achakulvisut, T., Adeyemi, A., Akrami, A., Alicea, B., Alonso-Andres, A., … & Vishne, G. (2022). Neuromatch Academy: a 3-week, online summer school in computational neuroscience. Journal of Open Source Education, 5(49), 118.
Lagaris, I. E., Likas, A., & Fotiadis, D. I. (1998). Artificial Neural Networks for Solving Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 9(5), 987–1000. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.712178
Lee, H., & Kang, I. S. (1990). Neural algorithm for solving differential equations. Journal of Computational Physics, 91(1), 110–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(90)90007-N
Lusch, B., Kutz, J. N., & Brunton, S. L. (2018). Deep learning for universal linear embeddings of nonlinear dynamics. Nature communications, 9(1), 4950.
Meade, A. J., & Fernandez, A. A. (1994). The numerical solution of linear ordinary differential equations by feedforward neural networks. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 19(12), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0895-7177(94)90095-7
Supplementary Video Lectures#
Strogatz. S., (2021, March 1). Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos - Steven Strogatz, Cornell University [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLbN57C5Zdl6j_qJA-pARJnKsmROzPnO9V
Brunton, S. (2023, July 17th) Dynamical Systems (with Machine Learning) Playlist. https://www.youtube.com/@Eigensteve
Bramburger, J. (2023 September 1st) Data-Driven Methods for Dynamic System https://www.youtube.com/@jasonbramburger
Neuromatch Academy: Deep Learning https://deeplearning.neuromatch.io/tutorials/intro.html
Popular Videos#
The Relationship Equation - Numberphile. (2015, April 3). [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BkOIw7vAZCQ
How Wolves Change Rivers. (2014, February 13). [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysa5OBhXz-Q
Popular Press Reading#
Fry, H. (2018) Hello World: How to be Human in the Age of the Machine, Doubleday
Lindsay, G. (2021) Models of the Mind: How Physics, Engineering, and Mathematics Have Shaped Our Understanding of the Brain, MIT Press
Mitchell M, (2019) Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans, Pelican Books.
Strogatz, S. (2004). Sync: The emerging science of spontaneous order. Penguin UK.
Sokol, J, (2019). The Hidden Heroines of Chaos Quanta Magazine https://www.quantamagazine.org/hidden-heroines-of-chaos-ellen-fetter-and-margaret-hamilton-20190520/
Zurn, P., & Bassett, D. S. (2022) Curious minds: The power of connection. MIT Press.
Podcasts#
Strogatz, S. (2019-2021). Joy of X. Quanta Magazine. https://www.quantamagazine.org/tag/the-joy-of-x
Strogatz, S. (2022-). Joy of Why. Quanta Magazine. https://www.quantamagazine.org/tag/the-joy-of-x
In Our Time, (2014). e, BBC Radio 4 https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/b04hz49f
Deep Mind: Podcast, https://deepmind.com/blog/article/welcome-to-the-deepmind-podcast
The Function Room (2021-) https://www.colmoregan.com/listen
Brain Inspired (2018-)https://braininspired.co/about/
Playlist#
Butler, J. S., (2023), Course Playlist https://open.spotify.com/playlist/2c20miz5iDpUNcNzbnDsbV?si=2f10b55408394993